Top Home Insurance Companies and Brokers in Canada
Pricing varies by product, Discounts on Home + Auto Bundles
Ontario Only
Pricing varies by product
British Columbia, Alberta, Saskatchewan, Manitoba, and Ontario
Pricing varies by product
All of Canada excluding Quebec
What is Home Insurance?
Home insurance is insurance against your personal, private property - both the dwelling itself, and its contents. This can be a home or a condo (or a rented apartment if you opt for tenant’ insurance). You, as the policyholder, pay a set fee (or premium) every month, in exchange for the insurance company (the insurer) covering the costs associated with any future unforeseen events. What’s covered by the policy is known as insured perils, and many policies come with a deductible - a small amount that you must pay upfront when making a claim.
Who Needs Home Insurance?
Almost everyone needs home insurance; the very definition of an unexpected event is that you can’t plan for it. Whether it’s a fallen tree hitting your roof, a burst pipe, a theft, or something else, the costs to fix the damage or replace your items can escalate quickly. Think of the value of your home; how much you paid for it, plus the work you’ve put into it, plus all the fixtures and fittings, plus all your furniture and contents and personal items. That’s a lot of value all in one place, and home insurance is the single easiest and most cost-effective way to protect it against risk.
For those who used a mortgage to purchase their home, you are probably required to have home insurance. Most mortgage companies have this as a prerequisite, so that in the event of a catastrophe, they won’t lose out either.
The Canadian System of Home Insurance
Canada has seven distinct levels of home insurance coverage, designated as A-G. These accumulate in coverage levels and cost.
Level A Coverage - Main Dwelling
This level covers just the physical structure of your home: the walls, foundation, floors, windows, doors and roof. The coverage is calculated by considering what it would cost to rebuild the building completely, from scratch. Note that this is not the same as how much you paid for it, or how much it is valued at on the open market.
Level B Coverage - Other Structures
This level includes other structures located on the property but that aren’t part of the main home - garages, sheds, workshops, and so on.
Level C Coverage - Contents
This coverage includes all of your personal contents of the home (and its attached structures). This means everything - jewellery, art, furniture, appliances, electronics, clothes, and so on, up to a set limit per item.
Level D Coverage - Additional Living Expenses
Level D covers costs incurred when you are living away from home due to an insurable event. For example, if your home floods and you have to relocate temporarily to a hotel, level D coverage would cover these costs.
Level E Coverage - Personal Liability
This is where the coverage starts to get more abstract; level E provides protection in the event that someone - anyone - is hurt or has their property damaged while in your home. So if someone falls down your stairs and incurs medical costs, this level would cover that eventuality.
Level F Coverage - Voluntary Medical Payments
Even more remote in possibility is if you have a visitor to your home and they are hurt by you, and you wish to voluntarily cover their medical expenses. This level is usually not required.
Level G Coverage - Voluntary Property Damage
This coverage can be used to cover the costs you incur when damaging another person’s property, anywhere else in the world. This is the most comprehensive level of coverage but is rarely used.
Add-Ons
There are also a lot of insurance add-ons that don’t fall within the guidelines of any of the above levels but that may be relevant to you. These include:
- Credit card theft or misuse
- Identity fraud
- Flood insurance (this may only be available if you don’t live in a flood zone)
- Lock repair and replacement
- Freezer food replacement
- Mass evacuation
- Counterfeit cheques and money
- Fire department charges
- Coverage for specific, high value items (such as jewellery, art, musical instruments and so on)
Understanding the Home Insurance Levels
Most people won’t know the level of home insurance they want or need when searching for a policy, so to simplify things, providers talk about what’s available in broader terms. Generally, home insurance policies fall into four major categories:
- No frills coverage, which covers just the physical dwelling itself (Level A); this is typically only used on properties that do not qualify for any other coverage.
- Standard coverage, which covers the most common events that can happen - known as named perils (Levels A-C).
- Broad coverage, which covers the entire property against all possible perils, and its contents against named perils (Levels A-E).
- Comprehensive coverage, which covers everything, including all personal liabilities and all risks (Levels A-G) .
Inclusions and Exclusions
Standard coverage, the most popular form of coverage, has set inclusions and exclusions. In particular, events that are covered are known as insured perils and include:
- Fire
- LightningÂ
- Smoke
- Theft
- Unpreventable water damage
- Wind
- Aircraft or vehicle impact
- Explosion
- Falling objects
There are some common exclusions too; some of these can be added onto your policy for an extra cost, but you should know that they have to be requested:
- Maintenance issues
- Sewer backup
- Flooding
- Pollution damage
- Water damage as a result of negligence
- Pest control and pest-caused damage
- Expensive collectibles and high value items
- Earthquakes, landslides, snow slides and sinkholes
- Recreational vehicles
- Acts of war and terrorism
- Foundation cracks
- Home-based business activities, liabilities and equipment
Different Insurers, Different Terms
Every insurer has slightly different terms when it comes to coverage; to make things trickier, they may even have different definitions of certain terms. What one company thinks of as an electrical surge may be defined differently elsewhere! So it’s incredibly important to read the terms of any home insurance policy, so you know what’s covered (and by how much), what’s excluded, your prohibited activities, and so on. This enables you to properly choose the coverage you need, identify add-ons if necessary, and choose your deductible.
Sound confusing? Don’t worry!
If all that sounds like a lot, don’t worry. Most insurance companies are incredibly on-the-ball when it comes to collecting the relevant information and helping you to understand the different levels of coverage you qualify for. Most will even be able to bring up basic details of your home based on your address! This makes the process of applying for and choosing coverage much smoother than you’d expect.
Frequently Asked Questions About Home Insurance
How much does home insurance cost?
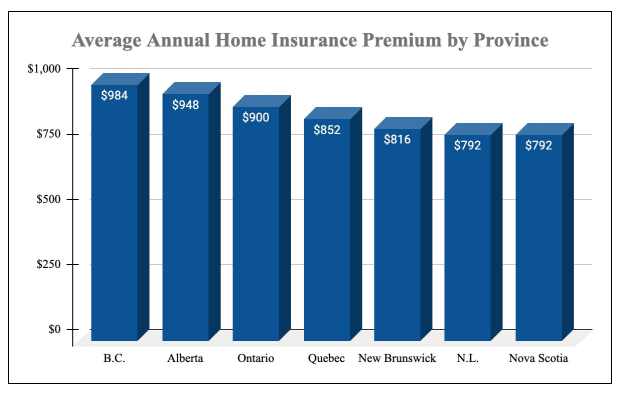
The cost of home insurance depends on a few factors:
- The cost of the home
- Where it is and its proximity to emergency services and fire hydrants
- The age of the roof (a new roof means you are less likely to suffer from water damage)
- Its source of heating (as this impacts the risk of fire)
- The age and state of your electrical wiring
- The age and state of your plumbing
- The presence of smoke alarms, CO alarms, home security systems, external structures and high-risk amenities such as a pool
- Your personal claims history
The most basic policies start as low as $10 a month, but the average Canadian spends $75 a month on premiums.
How much home insurance do I need?
The amount of home insurance you need depends on the value of your home and its contents. To get a rough estimate, take an inventory of everything in and of your home and calculate its value. If you have specific high value items, these might need to be covered separately.
Can I bundle my home insurance policy with other insurance policies?
It’s very common to bundle home insurance with other insurance policies, such as auto insurance or life insurance. This is by no means required, but bundling can provide access to discounts that help reduce your premiums while maintaining a high level of coverage.
How can I reduce my insurance premiums?
Reducing your home insurance premiums is something you can take an active step toward, by:
- Installing smoke and CO alarms
- Installing a home security system
- Opting for a higher deductible (a higher deductible means you will pay less for your monthly premiums, but will have to pay more out of pocket when you make a claim)
- Bundling the policy with other insurance policies from the same provider
- Maintaining good credit
- Making your home more disaster resistant (area dependent)
How does tenant insurance differ from home insurance?
Tenant insurance is available to people who are renting their home, and so do not need insurance for the physical building itself, just for their personal contents. This insurance therefore only covers the items you own in the home, and as such is generally cheaper than full home insurance.
Written By Smarter Loans Staff

The Smarter Loans Staff is made up of writers, researchers, journalists, business leaders and industry experts who carefully research, analyze and produce Canada's highest quality content when it comes to money matters, on behalf of Smarter Loans. While we cannot possibly name every person involved in the process, we collectively credit them as Smarter Loans Writing Staff. Our work has been featured in the Toronto Star, National Post and many other publications. Today, Smarter Loans is recognized in Canada as the go-to destination for financial education, and was named the "GPS of Fintech Lending" by the Toronto Star.
Discover Popular Financial Services
Why Choose Smarter Loans?

Access to Over 50 Lenders in One Place
Transparency in Rates & Terms

100% Free to Use
Apply Once & Get Multiple Offers
Save Time & Money
Expert Tips and Advice